Heating Elements / Electric Elements
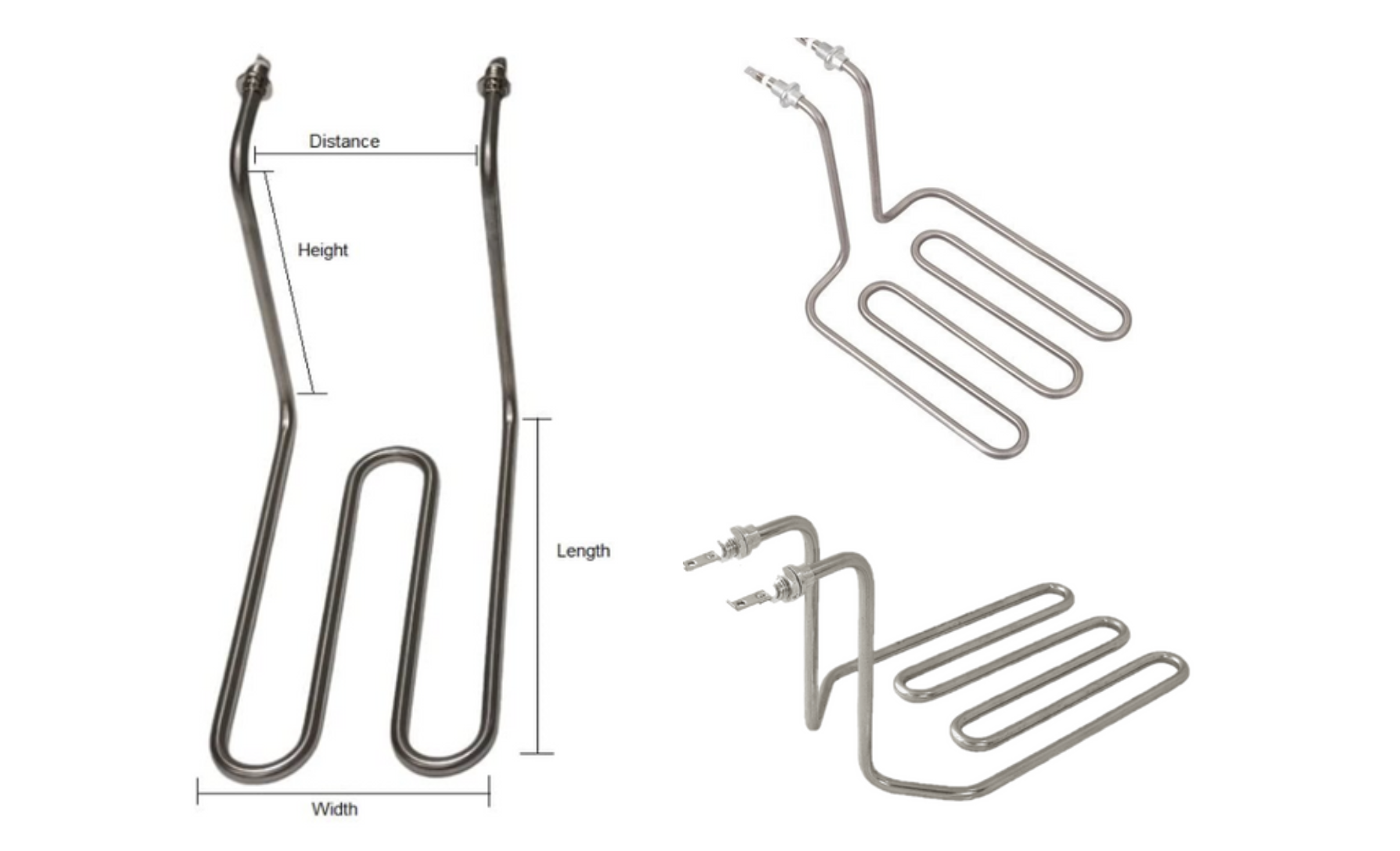
TUBULAR HEATING ELEMENTS
Tubular Heating Elements by Thermostat and Controls are versatile, dependable, and rugged heat sources for various applications. They are made of high-quality materials and are mineral insulated, metal-sheathed electric resistance heaters. These qualities make Tubular Heating Elements an ideal heat source for many applications. Tubular Heating Elements are the core of the most common heating solutions found today.
COMPONENTS
Thermostat and Controls uses 80-20 Nickle-chrome wire, “A” grade magnesium oxide, and the highest quality tubing. Filling machines and roll reduction equipment are expertly maintained to manufacturer’s tolerances, and final test equipment is fully calibrated. You can expect high quality from us.
Tubular Heating Elements have 4 basic components:
- Metal Sheath
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Helix resistance coil
- Cold section at each end
A variety of sheath materials are available for different application conditions. These take into account corrosion and temperature factors. Let us help you choose the optimum sheath material to ensure the longest possible life for your application.
Sheath materials include:
- Steel
- Copper
- Titanium
- Incoloy 800®
- Incoloy 840®
- Inconel 600®
- 304 stainless steel
- 316 stainless steel
The heater element requires a cold section at each end to keep the electrical terminals from overheating. A steel pin of the desired length is used for this purpose. It is spot welded to the helix coil element for a secure connection. In the final step of assembly, the pin is exposed at each end of the element and is ready to accept a variety of terminal options.
FEATURES:
- Elements can be formed into almost any configuration
- Wide variety of wattages and voltages
- Wide variety of temination types
- Wide variety of sheath material
- Finned sheath optional
- High purity compacted MgO provides maximum heat conductivity
- Integral cold pins provides optimum in-current carrying capacity.
- Optional end seals
| Sheath Material | Max. Sheath Temp °F (°C) | Watt per Square Inch | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 350°F (175) | 50 | Water, Non-Corrosive Liquids |
| Copper-Clad Steel | 750°F (400) | 20 | Oils, Glycol, Molten Salts, Non-Corrosives |
| SS 304 | 1200°F (650) | 30 | Improved Corrosion Resistance over steel |
| SS 316 | 1200°F (650) | 30 | De-ionized water and some corrosives |
| Incoloy840 | 1600°F (870) | 40 | Corrosive liquids, air, Clamp-on |
| Incoloy800 | 1600°F (870) | 40 | Improved resistance to achloride attack, other corrosives |
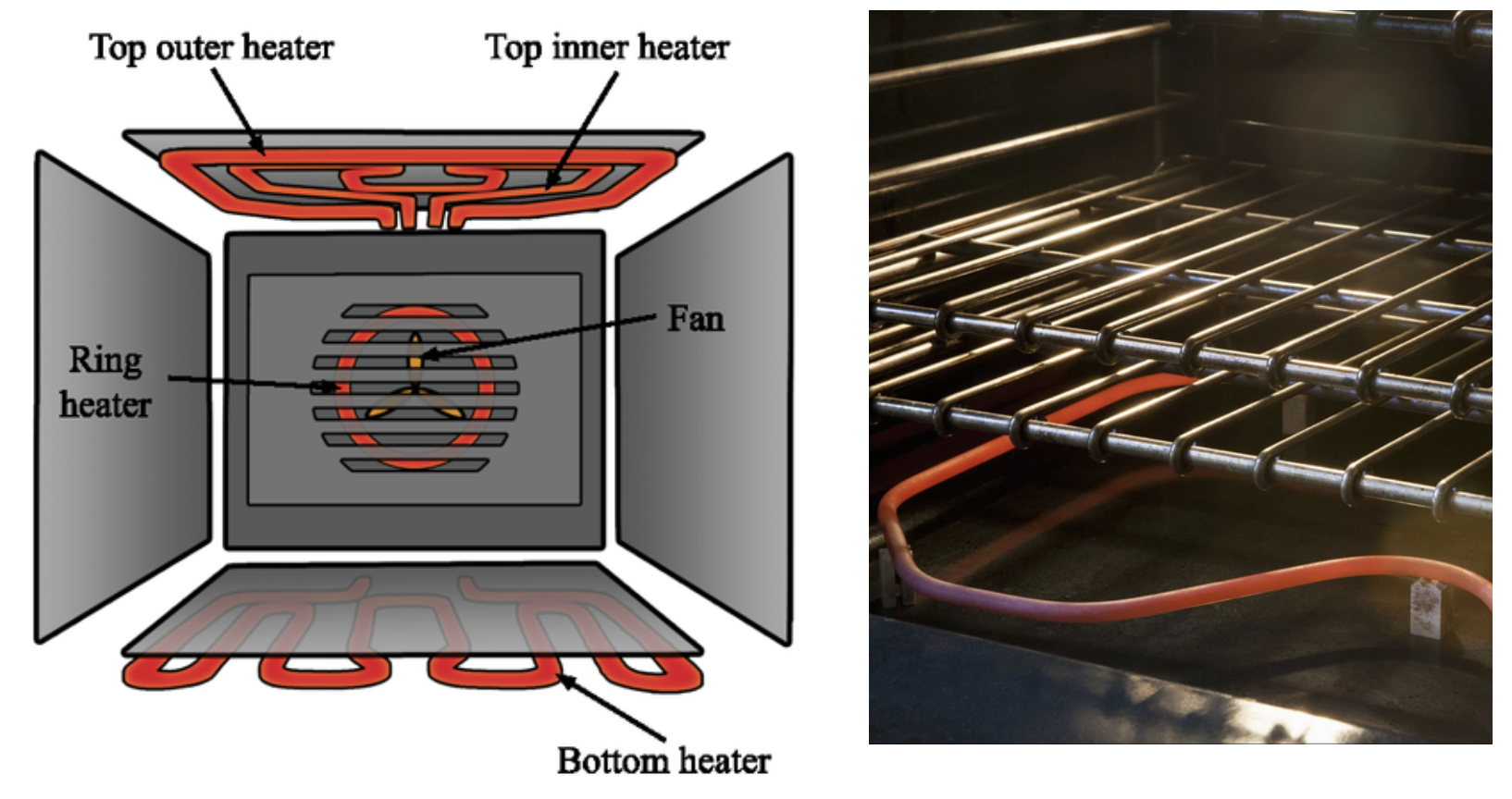
OVEN HEATING ELEMENTS
We manufacture premium electric oven heating elements with nickel-chrome wire Kanthal wire) for even heat distribution and grade A magnesium oxide for optimal thermal transfer and insulation. The elements offer different electrical terminations, mounting fittings, and bending options for seamless integration into any heating system.
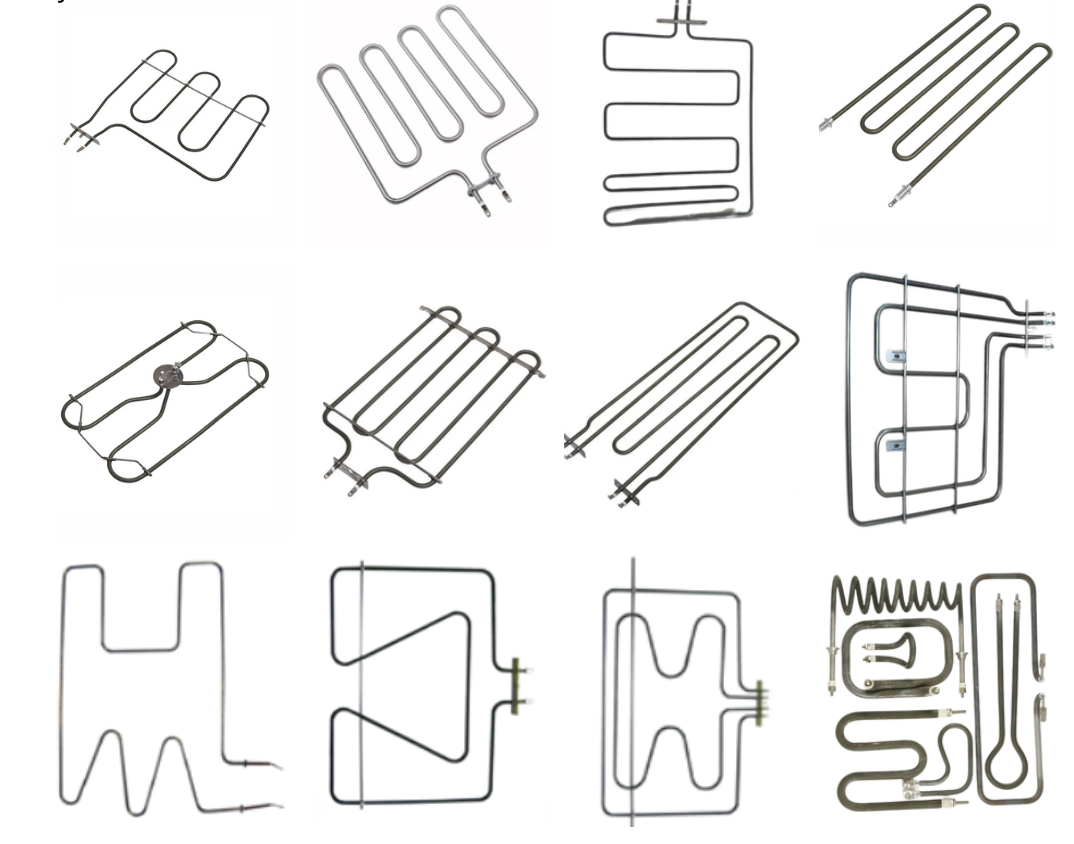
KEY FEATURES
- Construction: Tubular heating elements are tube-shaped with sealed ends and compactly wound heating wire.
- Heating Wire: Nichrome alloy is typically used for its high resistance and heat tolerance.
- Mounting: Elements can be installed along oven walls, at the bottom, or on top.
- Longevity: With proper maintenance, tubular heating elements are durable for long-term use, although they may wear out over time like any electrical component.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Material | SS304, SS316, Copper, Incoloy420, Incoloy800 |
|---|---|
| Tube Diameter | 6mm–11mm |
| Size | Customized |
| Voltage | 110V, 220V, Customized |
| Power | 1000W, 2000W, Customized |
| Shape | Customized as per requirements |
APPLICATIONS
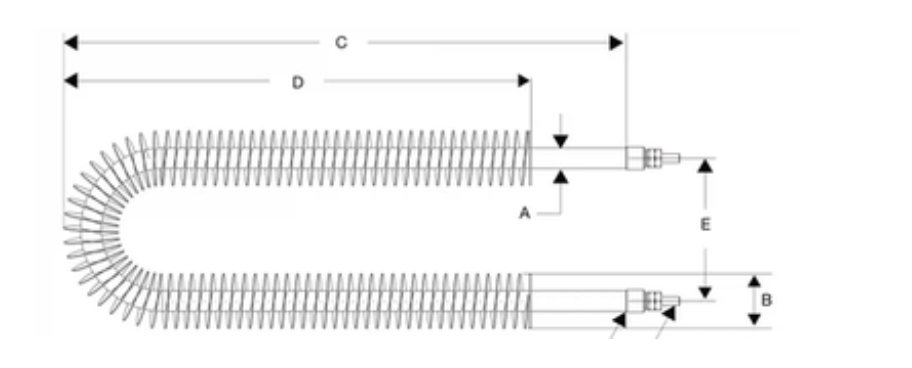
FINNED TUBULAR HEATER
Placing fins around tubular heaters enhances heat transfer capacity by increasing surface area. This design reduces heat loss, leading to rapid temperature rise, uniform heat distribution, and high thermal efficiency. We offer a user-friendly design for easy installation based on customer needs.
Straight Type Finned Tubular Heater

- Standard tubular heater with spiral fins to enhance surface area.
- Common size: 6-11mm diameter, 230V operation, fins 24-30mm in diameter.
- Custom sizes available upon request.

U Shaped Finned Tubular Heaters
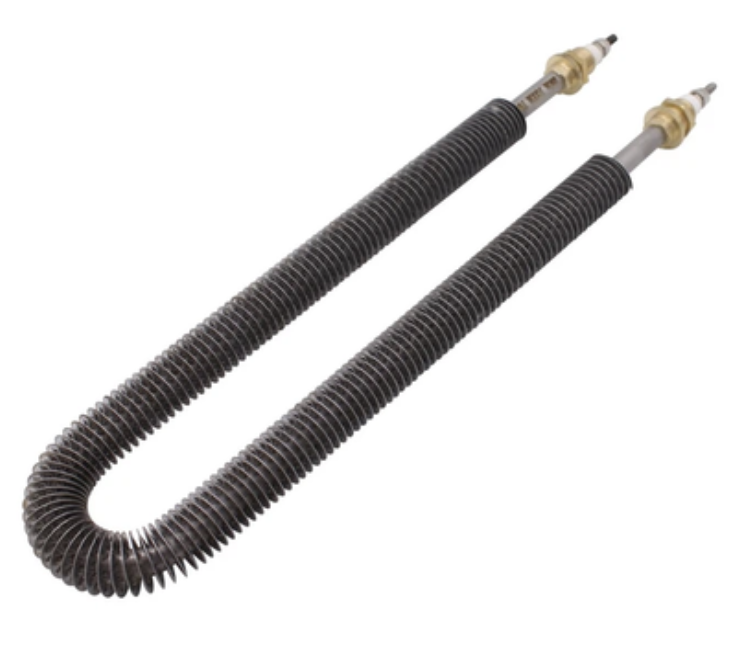

- Popular in air duct heating, oven heating, furnace operations, and load banks.
- Standard offering: 6-11mm diameter, 230V operation, 24-30mm spiral fins.
- Custom sizes available upon request.
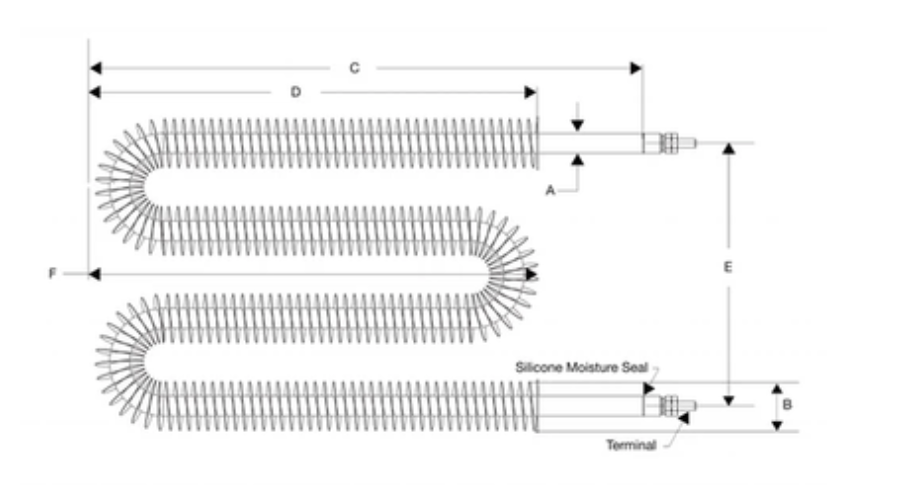
M Shaped Finned Tubular Heaters
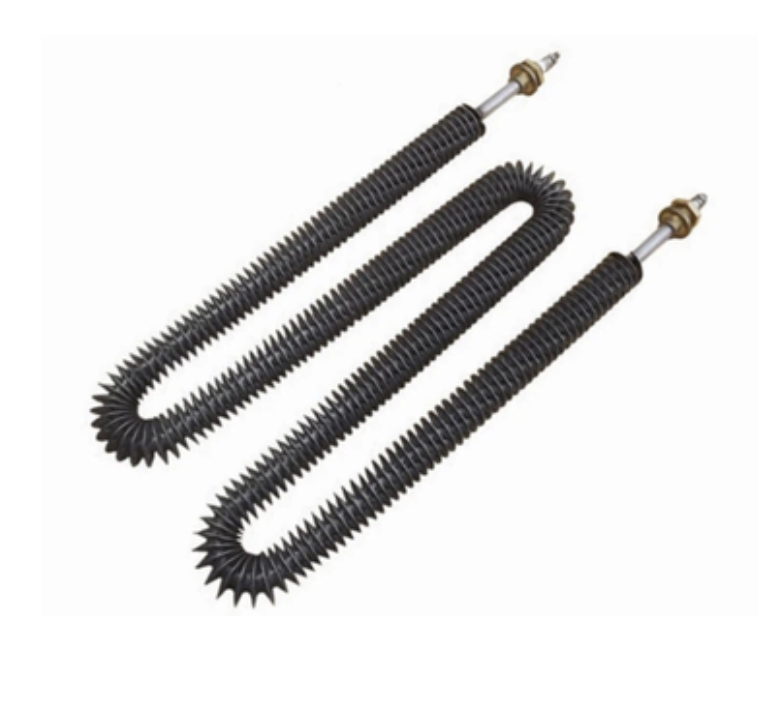

- Versatile W or M-shaped design optimized for tight spaces
- Customizable size, length, and R values
- Standard models: 6-11mm diameter, 230V, 24-30mm spiral fins
- Ability to accommodate custom dimensions upon request
SPECIFICATIONS
| Product Item | Finned Tubular Heating Elements |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 110V-600V, Or Customized |
| Sheath Watt Density | 2-13 w/cm2 |
| Sheath Material | SS304, SS316, Copper, Incoloy420, Incoloy800 |
| Fin Material | Mild Steel or Stainless steel |
| Sheath Lengths | 300mm to 3000mm or customized |
| Application | Air heater, used in oven and duct heater and other industry heating process |
COIL HEATING ELEMENTS
Coil heating elements are popular for electric stoves due to their flexibility in shape, high temperature capabilities, heating efficiency, quality, and durability.
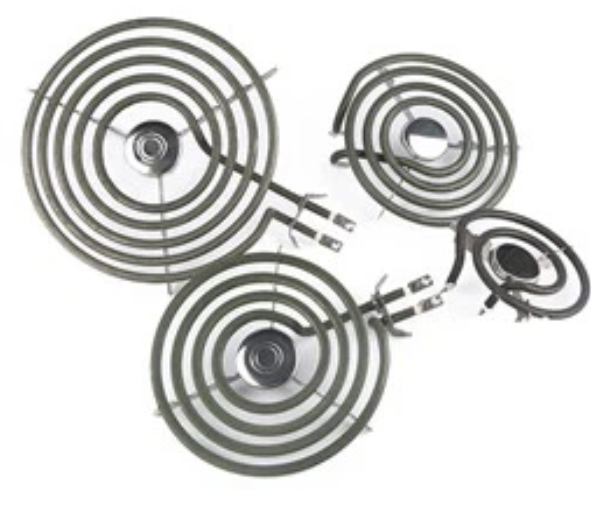
- Used in electric stovetops or cooktops
- Tubular metal element with coils for even heat distribution
- More turns lead to more even heat distribution, based on burner size and heating output
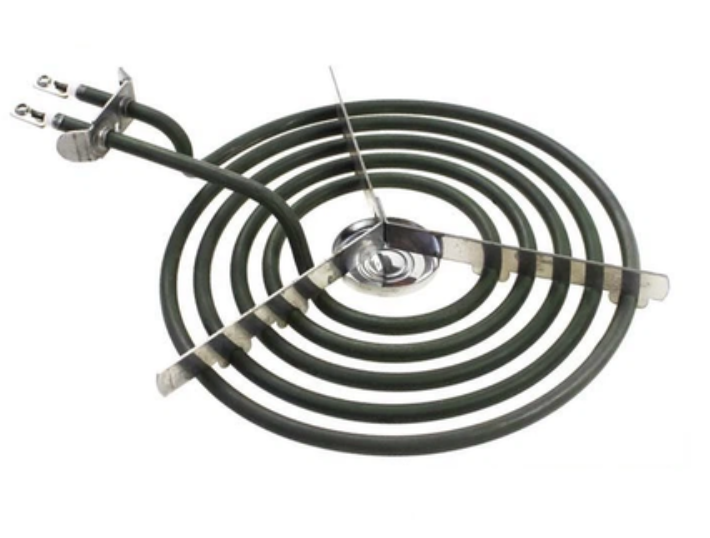

- Uses a metal tube shell with spiral electric heating alloy wires inside.
- Filled with magnesium oxide sand for insulation and heat conductivity.
- Sealed with silica gel or ceramic; can heat air, metal molds, and liquids.
- Includes additional structures like sealing, terminals, flange, and temperature control.
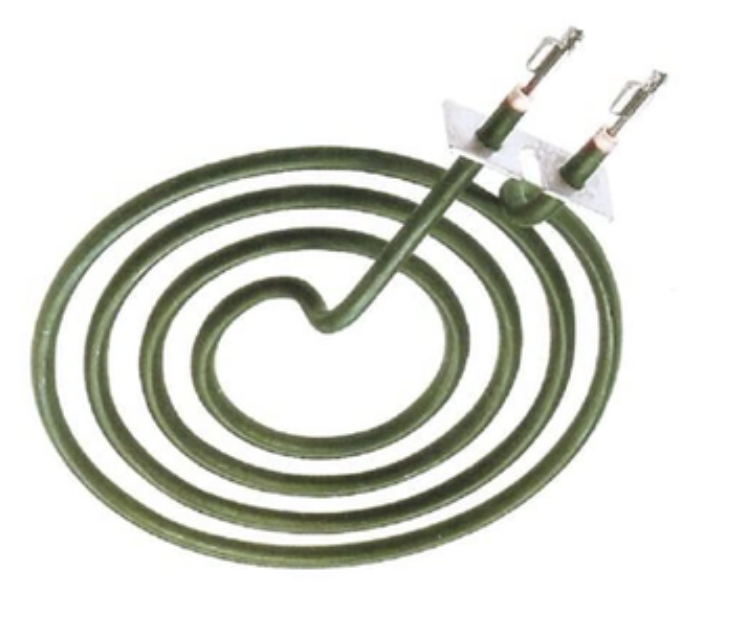

- Used widely in household kitchen equipment
- Available in copper, SS304, SS310, SS316, SS321 outer sheaths
- Features include excellent resistance wire and pure Mgo powder insulation
- Tubes can be bent into spiral shapes per customer requirements
COIL HEATING ELEMENTS
Coil heating elements are popular for electric stoves due to their flexibility in shape, high temperature capabilities, heating efficiency, quality, and durability.
APPLICATION

WATER HEATING ELEMENTS
Water electric heating elements come in different types like stainless steel, copper, or copper-coated pipes, efficiently heating water and solutions. We offer customized options for different shapes and sizes to meet specific client requirements, providing high-quality water heating elements for various applications.

120v 240v 480v 220v Heat Water Flange Immersion Heater Element is designed for heating liquids, gases, or mixtures based on customer process conditions. The design considers fluid type, temperature, pressure, heat exchange conditions, and environment. Heaters can be straight or L-shaped.

Water heating element is made of seamless stainless steel tubing, high-quality MgO, and high ohmic NiCr alloy wire. The heaters undergo advanced manufacturing and quality testing, ensuring fast temperature rise, uniform heating, and effective heating exchange for long-term use.
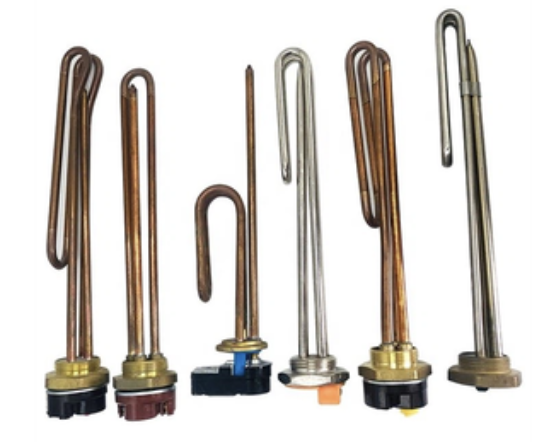

4500 Watt Water Heater Element is a popular type made to order. Benefits include reliable quality, reasonable price, stable performance, fast heating, low power consumption, long lifespan, and versatility in model and specification.

Water boilers are efficient heating elements used for water and air heating. Water heating requires a water environment and electricity, while air heating uses air as the main medium.
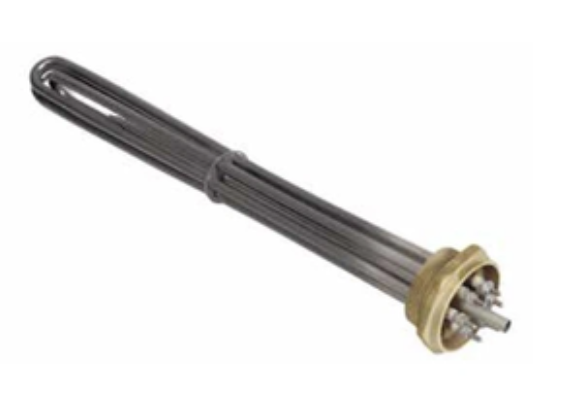

It is a metal tube with a central spiral electric heating alloy wire filled with insulating magnesia sand or ceramic. This electrical component converts energy for heating, known for being cost-effective, easy to install, and long-lasting (over 10,000 hours).
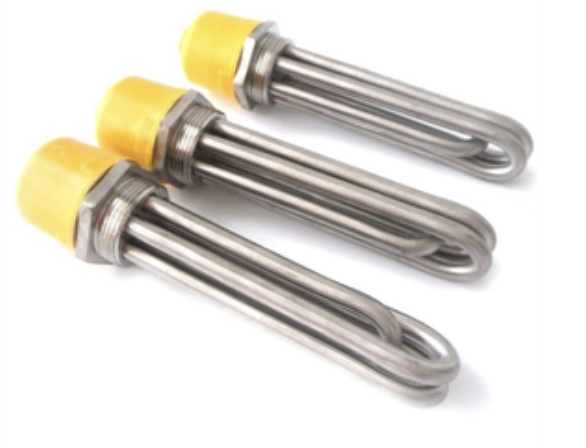

Immersion water heating elements are highly efficient as they directly heat liquids, oils, solvents, process solutions, molten materials, air, and gases, making them almost 100% energy efficient.

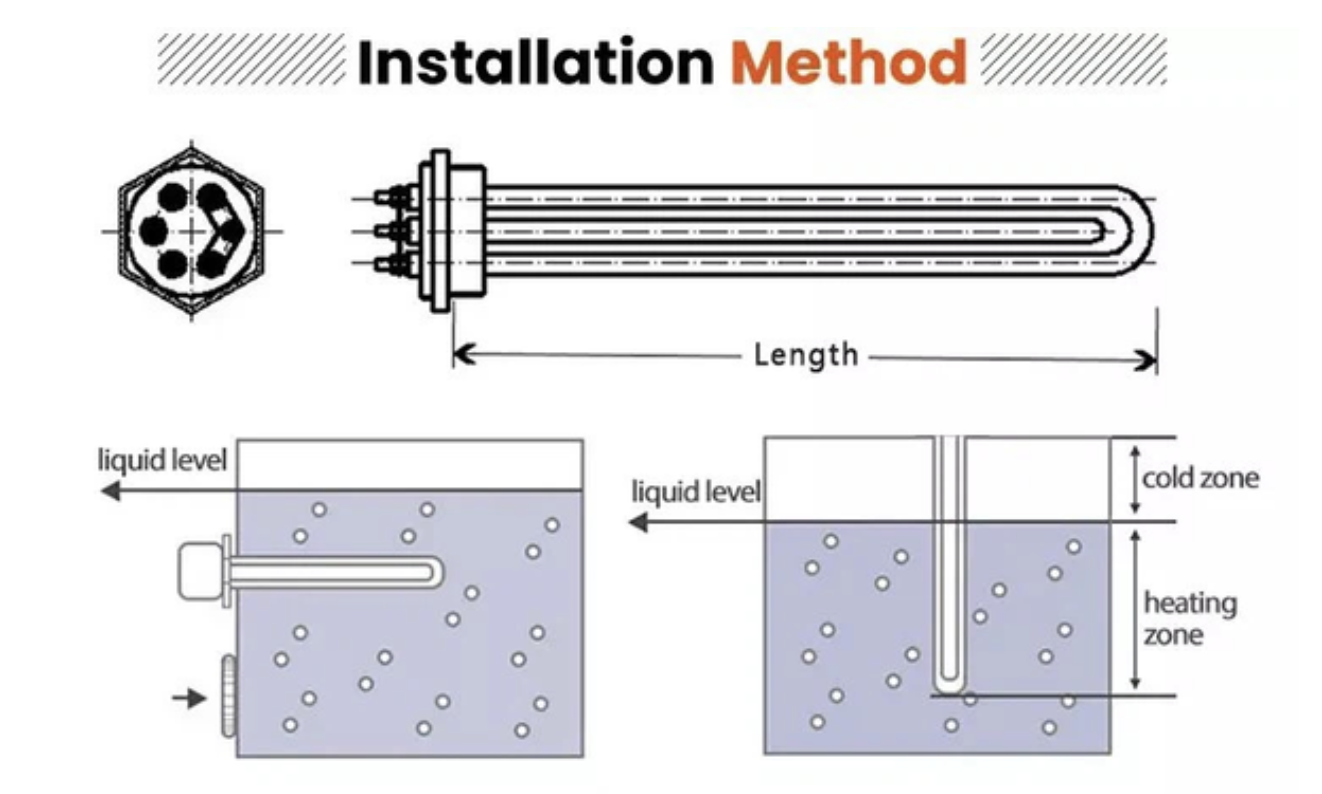
IMMERSION TUBULAR HEATERS
Immersion tubular heaters are versatile heating elements used in tanks and industrial equipment. They have tubular heating elements immersed in liquids or gases. Two common connections are screw plug heaters and flange connections, with materials like stainless steel and copper used. They are used in electric water boilers, solar energy systems, and various heating applications.
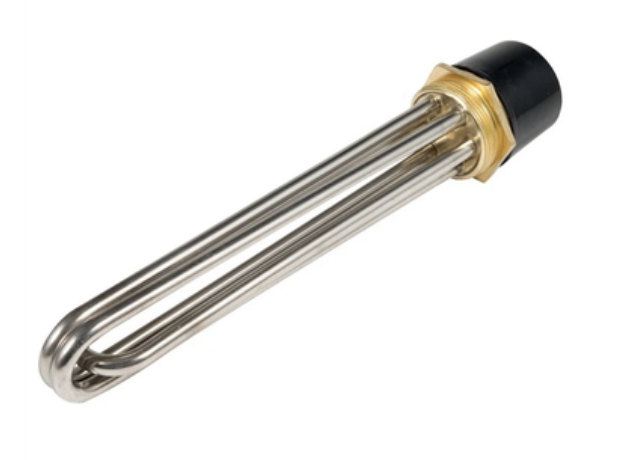

Screw Plug Immersion Heaters for Small Tanks use high-quality stainless steel materials like SS304, SS316L, Incoloy840, Incoloy800, and premium resistance wires. They heat liquids in tanks through groove side, flange, or threaded installation methods.
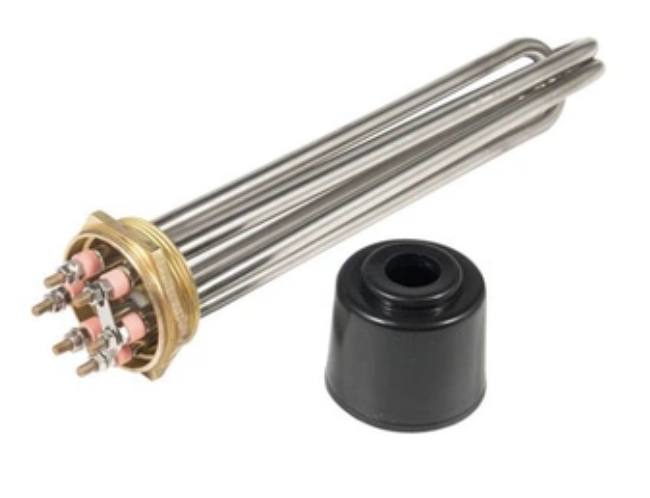

Immersion flange heating pipes consist of a resistive heating element enclosed in a protective sheath for durability and to prevent contamination. The flange is essential for securely mounting the heater to tanks, containers, or pipelines.
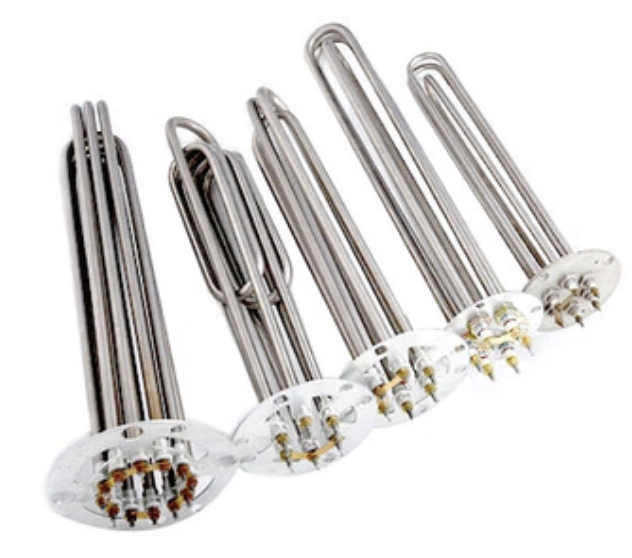

Flange immersion heaters are robust heating solutions designed for heating liquids and gases in large-scale industrial applications. They consist of tubular heating elements mounted onto a flange, which is then bolted to a tank or vessel, ensuring efficient and direct heat transfer.
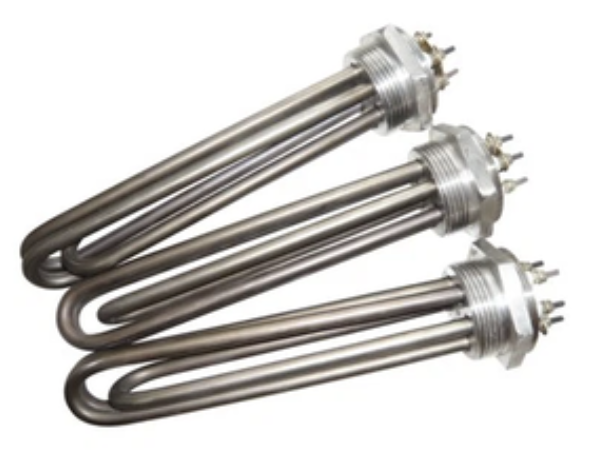

To use an immersion electric water heater, insert the heating element into water in a container like a bucket or bathtub. When connected to power, the element heats up, warming the water without requiring a dedicated water heating system.

The industrial inline water heater, also known as a flanged plate, connects pipes with flanges using bolts and gaskets for sealing. Flanges come in threaded and welding types.
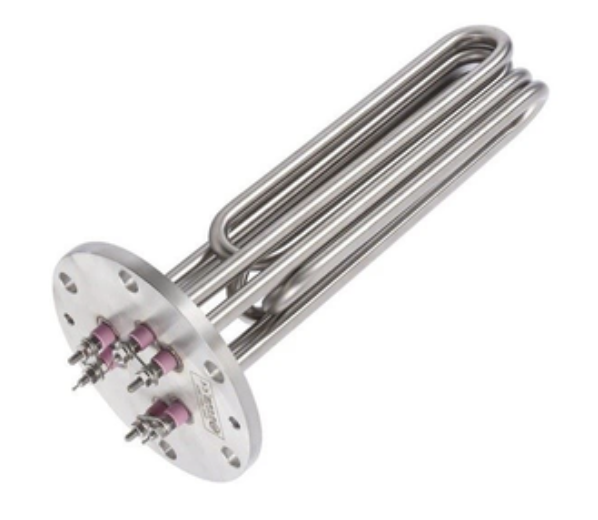

We created a high-power water tank tubular heater element for industrial use, operating at 380V with wattage options from 6KW to 18KW. It is made of SS304 material, 10mm diameter, around 500mm length (customizable), used for liquid tanks with brass or stainless steel flanges, quality heating parts, and ceramic insulation.
WASHING MACHINE HEATER
Washing machine heaters are custom-designed in a narrow M shape for roll drum type washing machines. They can include single or dual-phase thermal fuse micro-switches and NTC temperature control devices to regulate water temperature. Dryer heating elements are suitable for high temperature and humidity conditions.
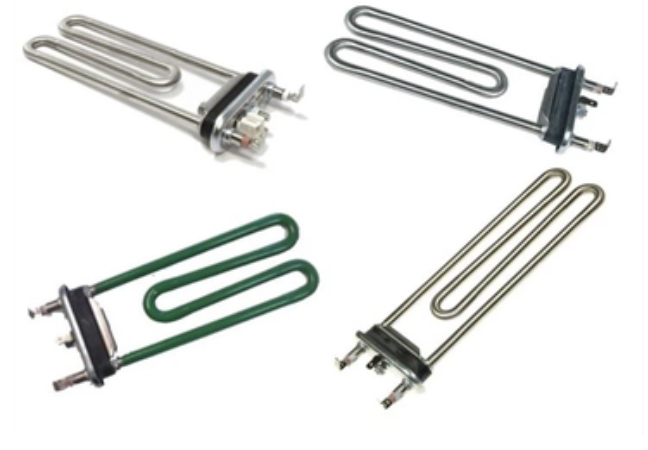

The product is a metal tube with spiral resistance wire and magnesium oxide powder, offering efficient heating for liquids, acid-base salts, and low-melting point metals. It has a robust structure, good thermal and mechanical properties, and can endure harsh conditions.
ADVANTAGES OF WASHING MACHINE HEATER
- Tubular heaters aid in effective cleaning by heating water for laundry.
- Hot water improves stain removal, breaks down tough stains, grease, and oil.
- Kills bacteria, germs, and dust mites for a hygienic clean.
- Versatile for different detergents and fabrics.
- Temperature control maintains consistent water temperature.
- Effective cleaning extends clothing lifespan.
- Removes allergens like pet dander and pollen.
- Reduces water hardness effects by dissolving minerals.
APPLICATION

IRON HEATER
The iron heater is suitable for iron and steam generators, featuring tubular and plate heaters made using advanced technology like stainless steel welding and aluminum casting. These electric heaters are used in various appliances like clothing irons and humidifiers, promising high efficiency, durability, and quality.
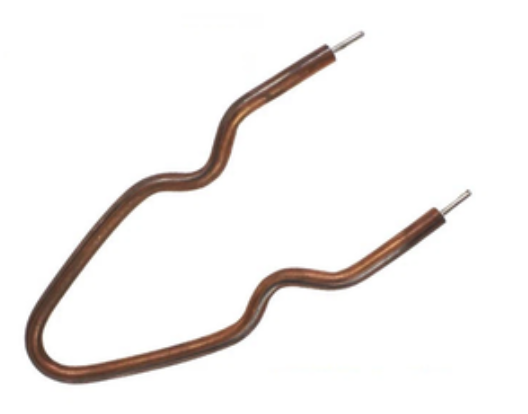

The electric iron heating element is crucial for clothes irons, offering high quality, even heating, fast speed, efficiency, durability, safety, and long lifespan. Widely used in small home appliances like clothing irons, coffee makers, and electric kettles.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Tube Diameter | 6–11mm diameter |
|---|---|
| Size | Customized |
| Resistance Wire | Ni80Cr20 Kanthal make |
| Sheath Material | SS304, SS316, Copper, Incoloy400, Incoloy820, Titanium |
| Insulation Material | Magnesium Oxide Powder |
| Voltage | 120–480V |
| Power | Customized |
FEATURES
- High heating effieciency
- Fast heating speed
- High Electrical Resistance
- Even heating
- Safety and reliable
- Long working life time
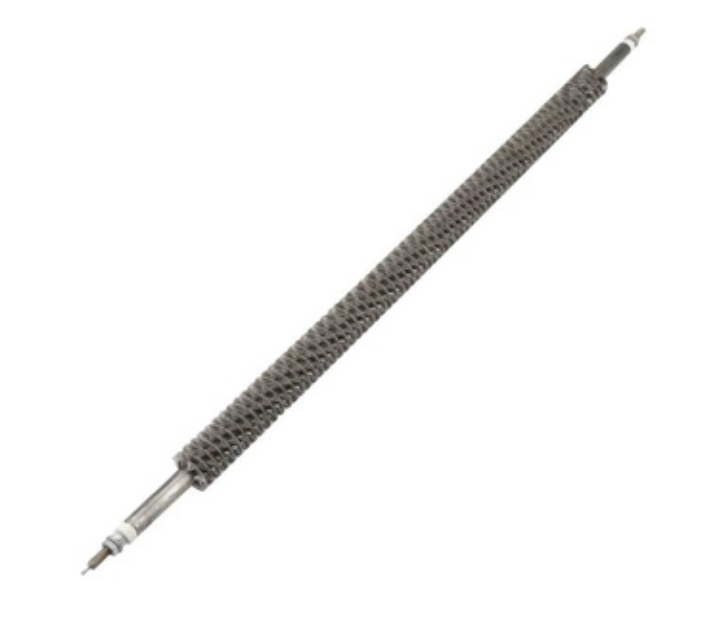
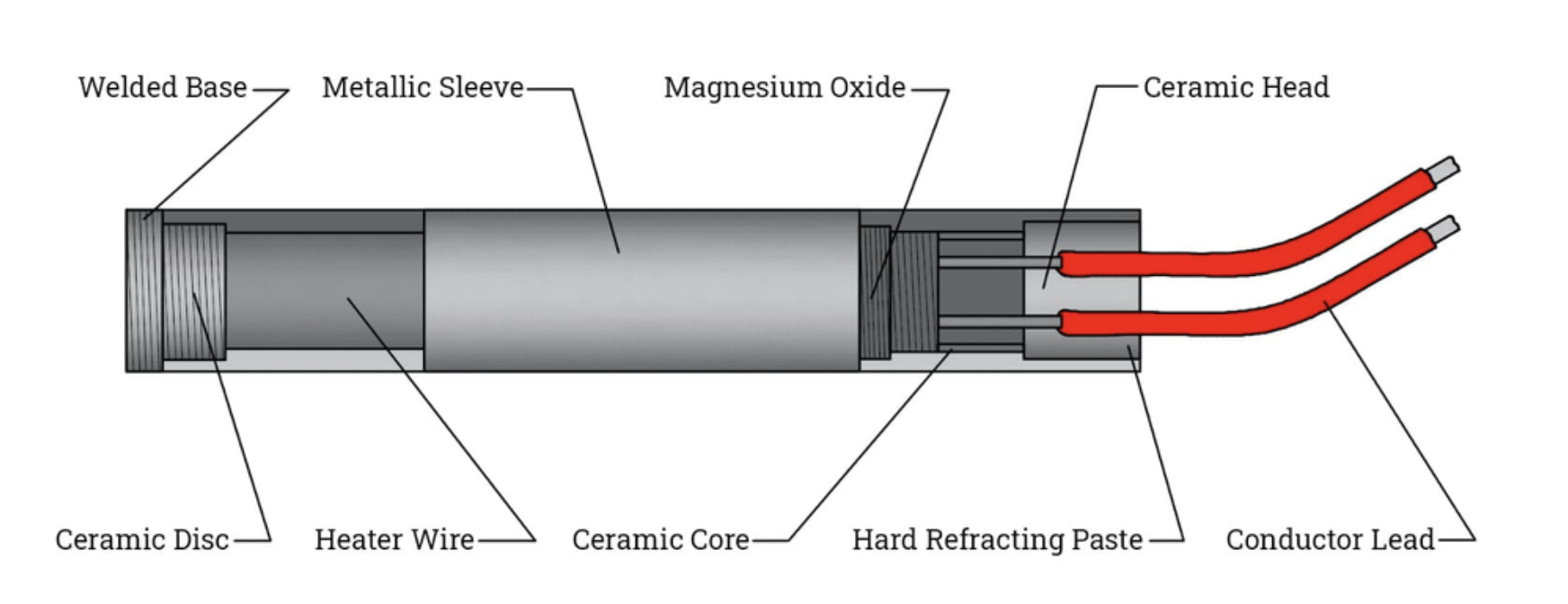
CARTRIDGE HEATER
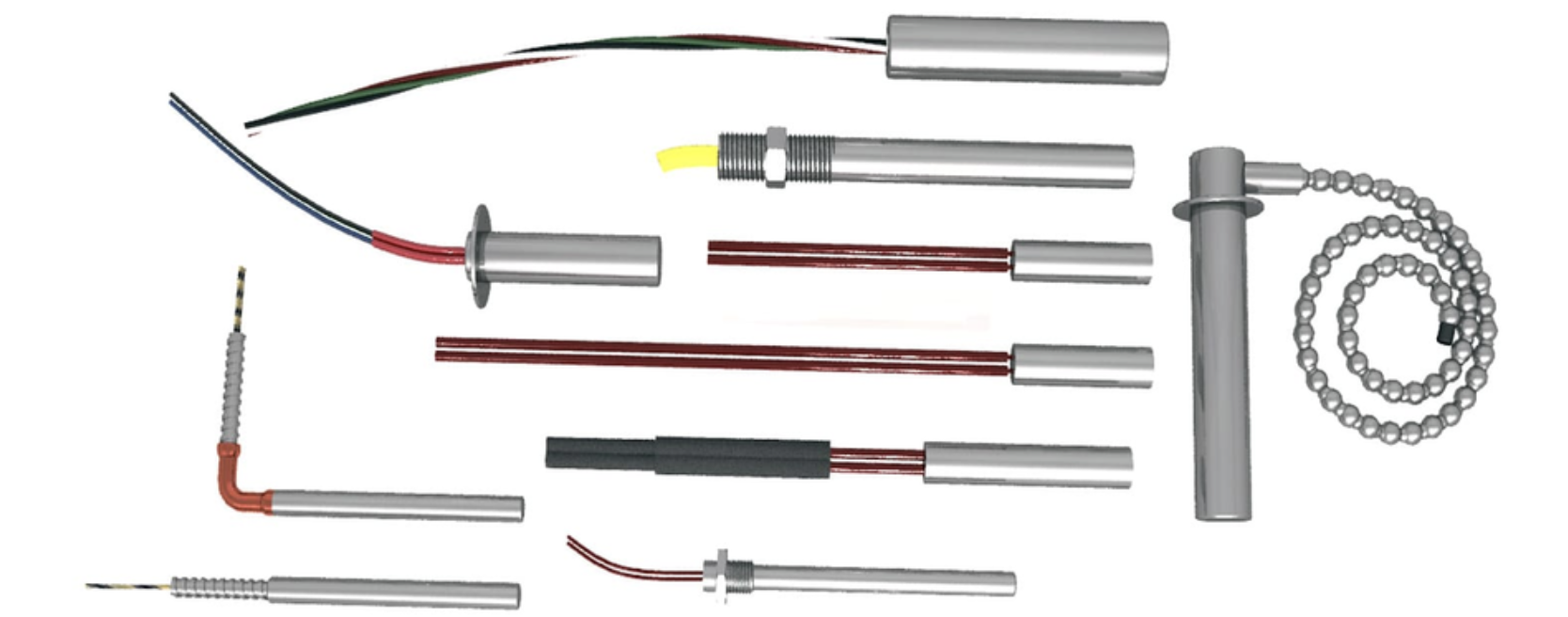
A cartridge heater is a tubular heating device used for precise heating in various applications. It is inserted into a hole to provide internal radiant heat, commonly used in manufacturing processes for localized heat. Cartridge heaters are easy to install, offer even heat distribution, and come in different watt densities to suit specific needs.
BENEFITS
- Flexibility
- Heavy Duty
- Accuracy
- Economical
- Over Heating
- Compact Design
SPECIFICATIONS
| Product name | Customized cartridge heaters |
|---|---|
| Resistance heating wire | NiCr 80/20 wire Kanthal make |
| Sheath material | SS304, SS316, Incoloy800, Incoloy840 |
| Maximum temperature | 800 degree Celsius |
| Voltage | 380V, 240V, 220V, 110V, 36V, 24V or 12V |
| Thermocouple Location | Type J, Type K |
APPLICATION
- Food processing
- Plastic moulds
- Medical equipment
- Hot stamping
- Liquid immersion
- Packaging equipment
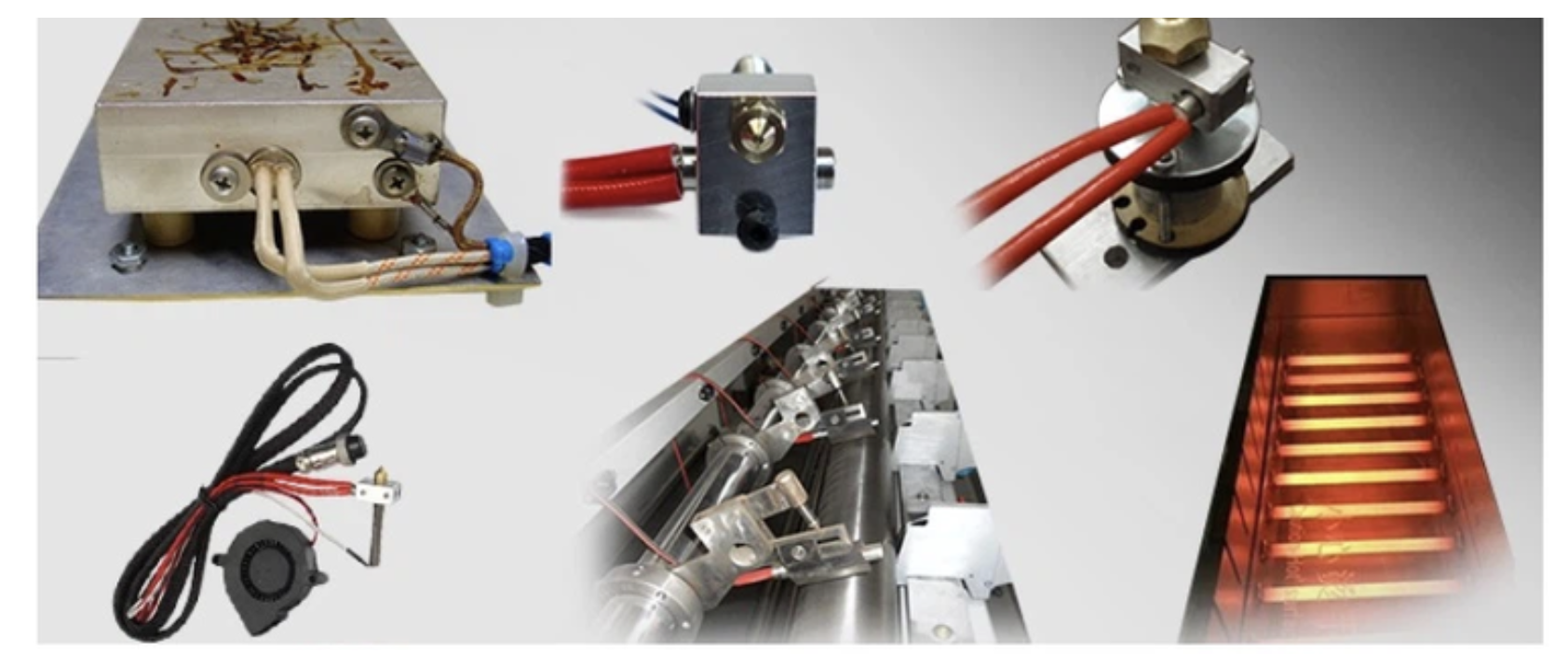

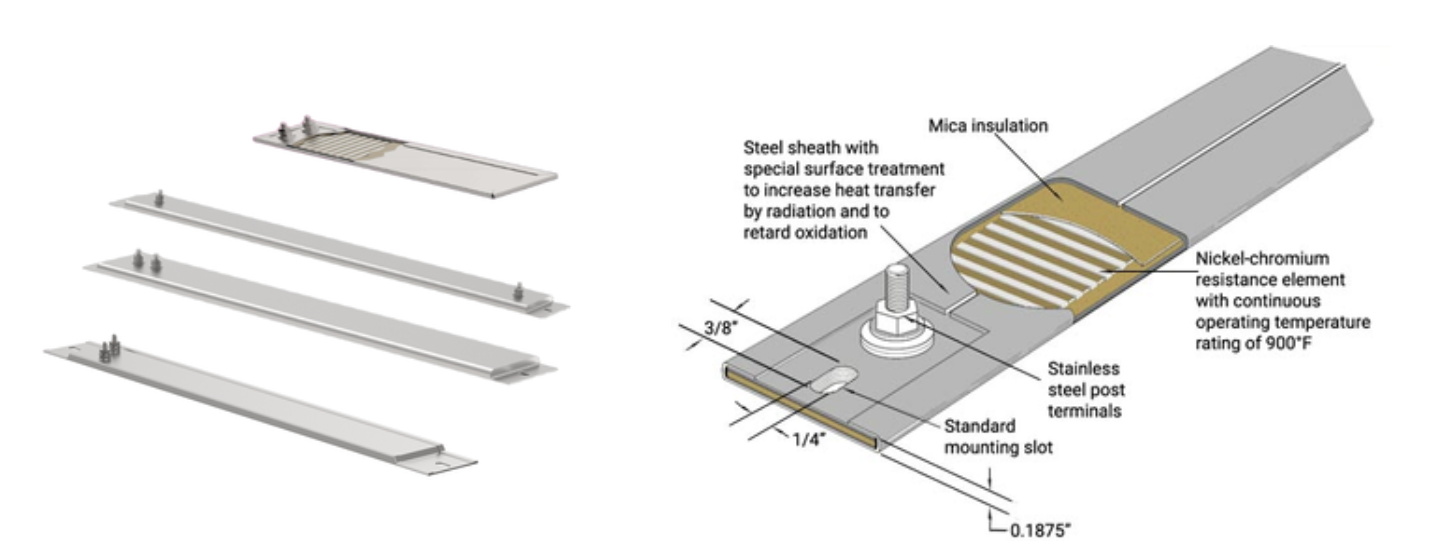
CERAMIC/MICA STRIP HEATER
MS plated SS or Brass sheath casting offers durability, high emissivity, and thermal conductivity for heater longevity. It uses a Nickel-Chromium Resistance wire and mica/ceramic insulation for excellent thermal conductivity and dielectric strength.
APPLICATION
- Warming Trays
- Food Processing
- Machinery Parts
- Dies and Molds
- Blow Molding Equipment
- Hot Plates
- Test Equipments
- Incubators
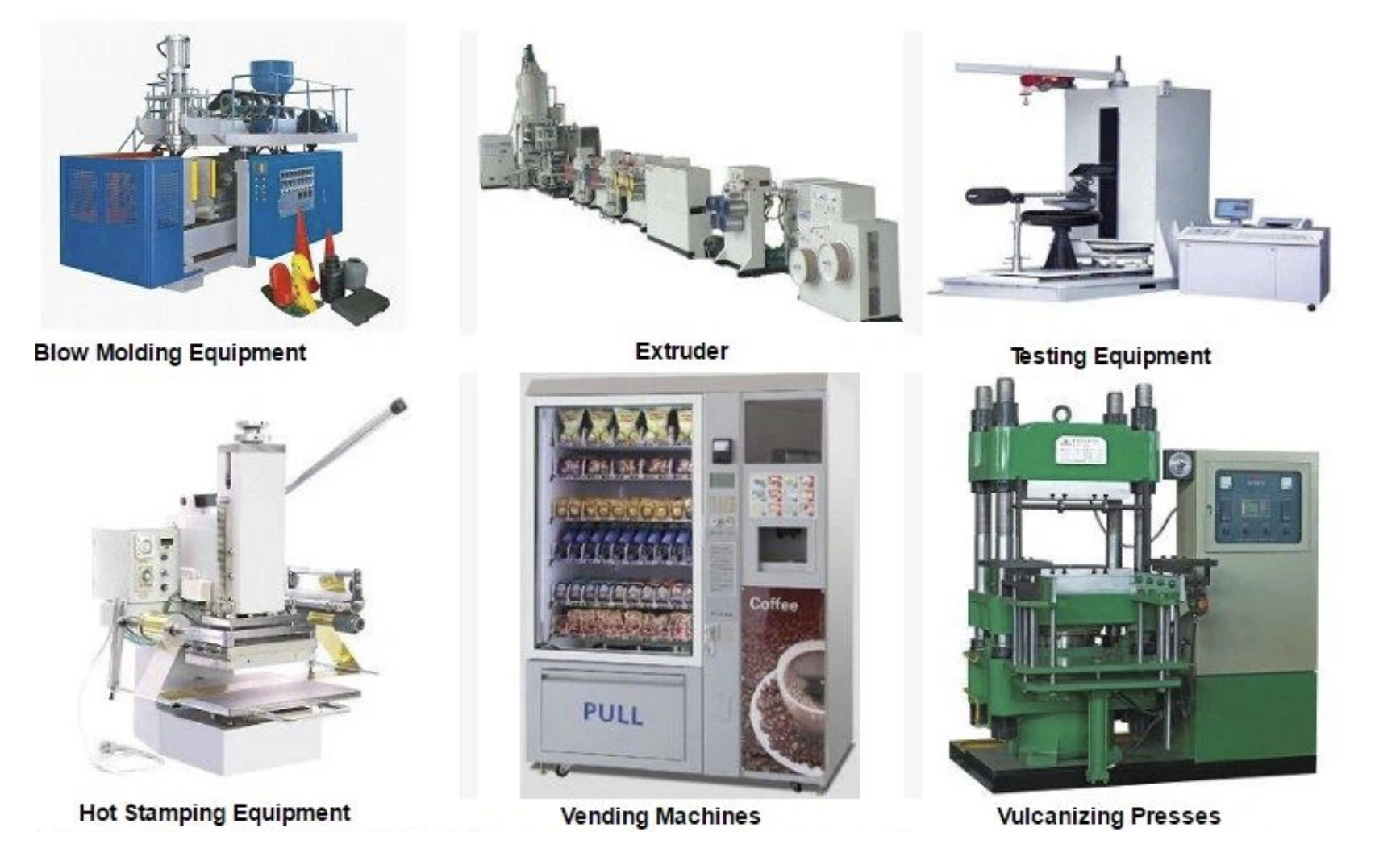

CERAMIC BAND HEATER
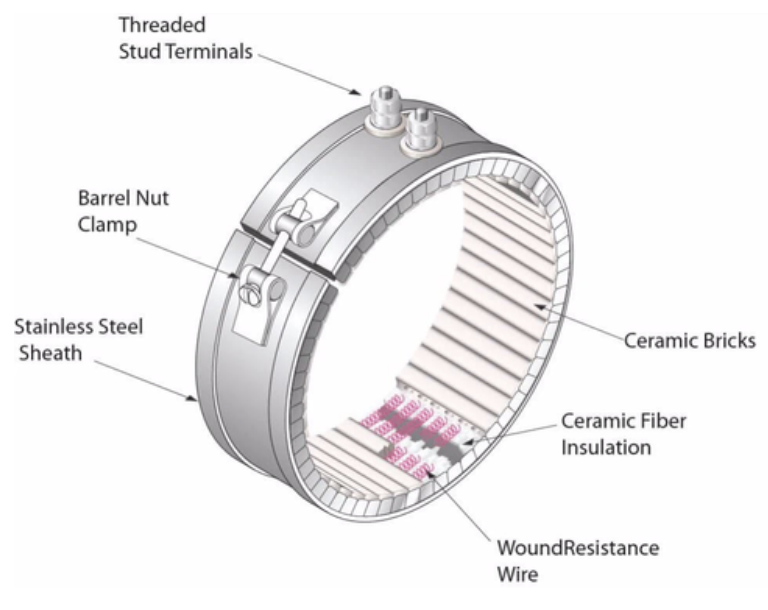
Stainless steel Ceramic Heating Band is made of stainless steel skin, and the ceramic with higher insulation and fire resistanceis put on a resistance wire, and then it is formed by mechanical twisting, and it can be used when it is turned on.
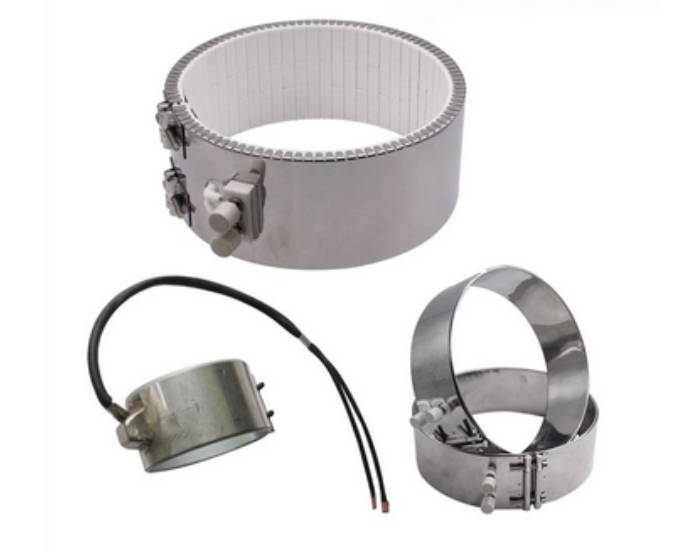

FEATURES
- Long perational Life.
- Energy saving
- Fast heat conduction
- Uniform heat distribution
- High electrical insulation
- Easy installation
- Great mechanical resistance to shocks
APPLICATION
- Plastics: Band heaters are crucial in plastic molding for precision heating to shape materials.
- Food Production: Band heaters aid chefs in heating ingredients evenly for proper cooking and mixing.
- Packaging: Band heaters are used for sealing and shrinking packaging materials quickly and efficiently.
- Pharmaceuticals: Band heaters ensure precise temperature control for producing uncontaminated medicines.
- Chemical Processing: Drum band heaters help maintain desired temperatures, reduce viscosity, and aid heat transfer.
- Industrial Equipment Heating: Band heaters regulate reactions, maintain viscosity, and prevent freezing in industrial equipment.
- Metal Casting: Band heaters are used to heat molds and materials for metal casting processes.
NOZZLE BAND HEATER
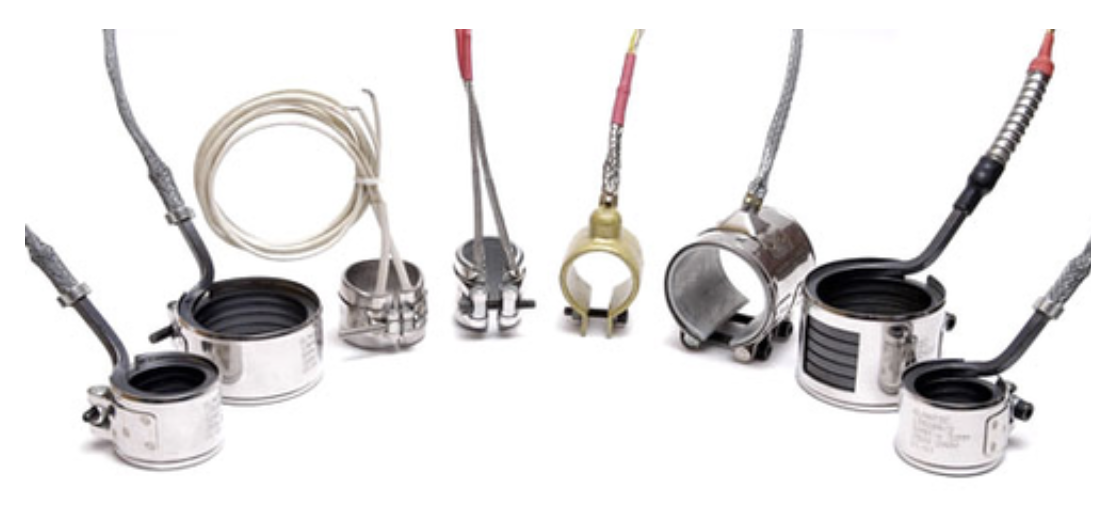

Nozzle band heaters come in mica, ceramic, micro tubular, and sealed types, with options for built-in thermocouples. They vary in dimensions, wattage, voltages, and materials, and can be customized.
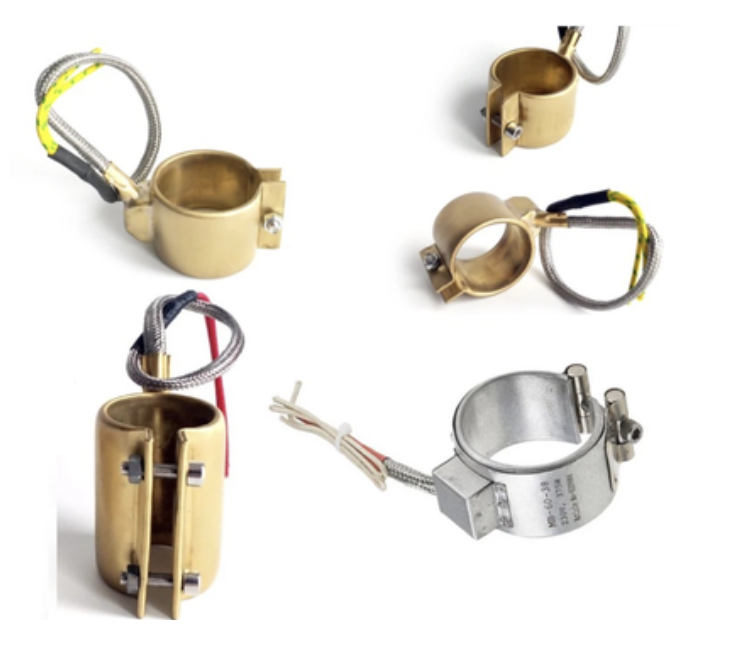

Brass nozzle band heaters are designed for Blow Molding Machines to provide precise and consistent heating to the machine's nozzle. They are made of brass for good thermal conductivity and durability, with a heating element typically composed of nichrome wire or a high-resistance alloy.
APPLICATION

